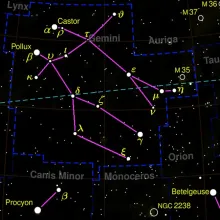
Constellation Gemini
Gemini is one of the twelve zodiac constellations, representing the twins Castor and Pollux from Greek mythology. It is a prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere and is located between Taurus and Cancer. The constellation is best known for its two brightest stars, Castor and Pollux, which represent the heads of the twins. The rest of the constellation forms a rough rectangle shape, symbolizing the bodies of the twins.