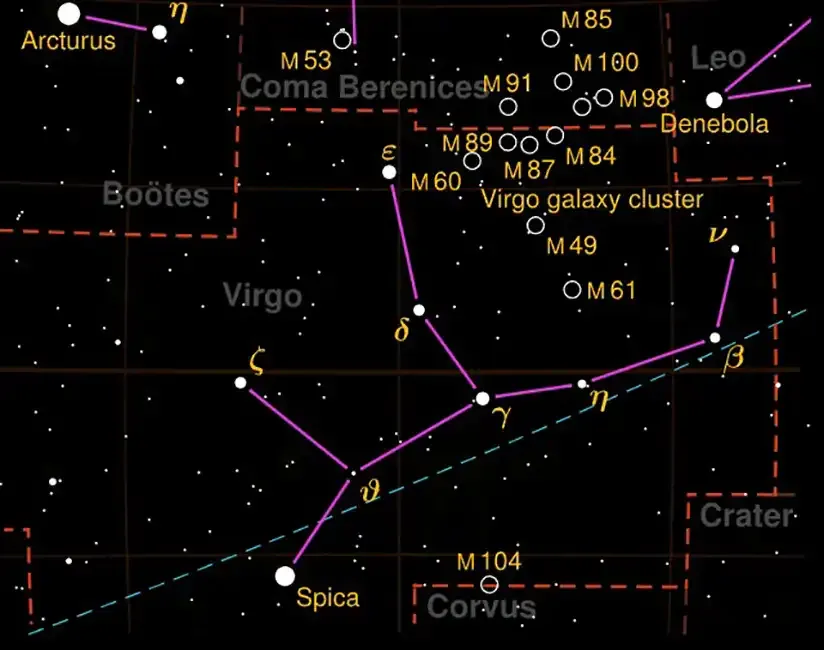
Virgo is the second-largest constellation in the sky, occupying an area of 1,294 square degrees. It's one of the 12 zodiac constellations and is often depicted as a maiden holding a sheaf of wheat. Virgo is positioned between Leo to the west and Libra to the east. This constellation is located in the southern celestial hemisphere but is visible from most parts of the world.
Key Features
- Area: 1,294 square degrees (2nd largest constellation)
- Position: RA 13h, Dec -2°
- Best Viewing Time: April to June
- Neighbors: Libra, Leo, Boötes, Hydra, Corvus, Serpens Caput
Mythology
In Greek mythology, Virgo is often associated with Demeter, the goddess of agriculture, or her daughter Persephone. According to myth, Persephone was abducted by Hades, leading Demeter to neglect the earth, causing winter. When Persephone was allowed to return, Demeter restored fertility to the earth, symbolizing the return of spring. This story ties Virgo to themes of harvest and fertility, as the maiden often carries a sheaf of wheat.
Notable Stars
- Spica (α Virginis): The brightest star in Virgo and the 15th brightest star in the night sky, Spica is a blue giant approximately 250 light-years away. It marks the ear of wheat in Virgo’s hand.
- Porrima (γ Virginis): A binary star system located about 38 light-years from Earth, easily visible with a small telescope.
- Vindemiatrix (ε Virginis): A yellow giant star, named after the Latin word for "grape-harvestress," symbolizing the connection of Virgo to the harvest.
- Zaniah (η Virginis): A triple star system that is part of Virgo’s figure.
- Heze (ζ Virginis): A distant white star that completes Virgo’s outline.
Visibility
Virgo is best viewed in the spring, particularly in April and May. It can be seen from both hemispheres, though it is best observed from the northern hemisphere during the evening hours. In the southern hemisphere, Virgo is visible high in the sky during late autumn.
Tips for Observing
- Location: Find a dark sky location away from city lights for the best view.
- Time: The best time to observe Virgo is in the late spring, around midnight.
- Tools: While Spica is bright and easily visible with the naked eye, using a pair of binoculars or a small telescope can help you spot the fainter stars and details within the constellation, including the many galaxies that are part of the Virgo Cluster.
- Landmarks: Start by locating Spica, which is the brightest star in Virgo, to help orient yourself within the constellation.
- Galaxies: Virgo is home to the Virgo Cluster, a collection of galaxies that includes the famous M87, which is observable with a medium-sized telescope.
