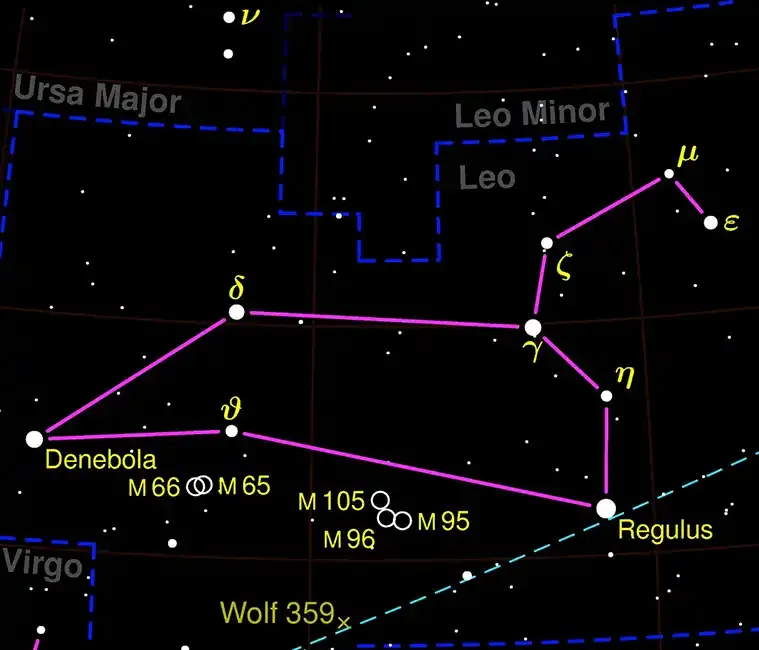
Leo is one of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky, primarily because of its distinctive shape, which resembles a crouching lion. It is a prominent constellation in the zodiac, meaning that the Sun passes through it during the year. Leo is visible in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, making it accessible to a wide range of observers.
Key Features
The constellation Leo is often visualized as a lion lying down, with its head and mane forming a distinctive backward question mark or sickle shape, and its body stretching out behind.
Mythology
In Greek mythology, Leo is associated with the Nemean Lion, a fearsome beast slain by Hercules as one of his Twelve Labors. The lion's hide was impervious to weapons, but Hercules managed to defeat it using his immense strength. After killing the lion, Hercules wore its skin as armor. Zeus placed the lion in the sky as a constellation to honor the hero’s achievement.
Notable Stars
- Regulus (Alpha Leonis): A blue-white main-sequence star about 79 light-years from Earth. It is part of a multiple star system with at least three other stars.
- Denebola (Beta Leonis): A white star about 36 light-years away, forming the lion's tail.
- Algieba (Gamma Leonis): A binary star system approximately 130 light-years from Earth, famous for its contrasting colors when viewed through a telescope.
Visibility
Leo is best viewed in the Northern Hemisphere during spring, particularly in April. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is best seen during late autumn. Leo is visible from latitudes between +90° and -65°, making it accessible to most of the world’s population.
Tips for Observing
- Location: Find a dark location away from city lights to fully appreciate Leo’s distinct shape and bright stars.
- Best Time to Observe: Leo rises in the east in the evening during late winter and is visible high in the southern sky in the spring.
- Tools: While Leo’s brightest stars can be seen with the naked eye, a small telescope or binoculars can enhance the viewing experience, especially for binary stars like Algieba.
