Orion
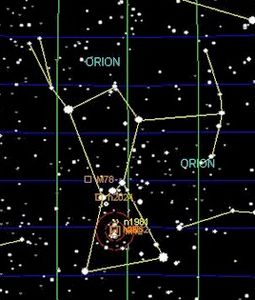
Orion the Hunter is a recognizable constellation in the winter sky. Orion's bright stars include: Rigel, Betelgeuse, Bellatrix, and Saiph, plus Alnilam, Alnitak, and Minitaka which form his belt. The most famous object in this constellation is M42, the Great Orion Nebula. One of the brightest deep-sky objects, this diffuse nebula is a massive star-forming region. The Horsehead Nebula, IC 434, is another popular feature of Orion, located near the star on the farthest left of the belt, Alnitak. The constellation of Orion is best viewed in January at 9:00 p.m.
Orion is also host to the Orionids meteor shower, which occurs annually in late October. This meteor shower is caused when the earth encounters dust particles from Halley's Comet. There are usually ten to fifteen meteors per hour during the peak of the Orionids.
- Messier 42 (M42) - The Orion Nebula: A diffuse nebula and one of the brightest nebulae in the sky, located in the sword of Orion.
- Messier 43 (M43) - De Mairan's Nebula: A part of the Orion Nebula, separated by a dark lane of dust, located just north of M42.
- Messier 78 (M78) - A reflection nebula located in Orion's belt region.
Canis Major
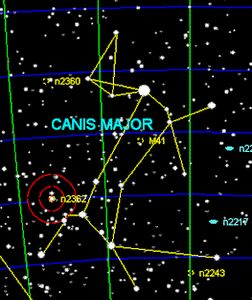
Canis Major is a small constellation of the southern hemisphere. Canis Major contains several bright stars. Sirius, the brightest of all the star\s belongs to this constellation. It borders to Monoceros in the north, Leus to the west and Columba to the southwest while the eastern border is covered by Puppis, Together with Prokyon and Betelgeuze, Sirius forms the so called Winter Triangle.
- NGC 2359 (Thor's Helmet)
- Type: Emission Nebula
- Description: A bubble-shaped nebula powered by a massive Wolf-Rayet star.
- NGC 2207 and IC 2163
- Type: Interacting Galaxies
- Description: A pair of interacting spiral galaxies.
- Messier 41 (M41)
- Type: Open Cluster
- Description: Located 4 degrees south of Sirius, this cluster contains around 100 stars, including several red giants.
- NGC 2360 (Caroline's Cluster)
- Type: Open Cluster
- Description: A rich open cluster discovered by Caroline Herschel.
- NGC 2362
- Type: Open Cluster
- Description: A young open cluster centered around the bright star Tau Canis Majoris.
- NGC 2354
- Type: Open Cluster
- Description: A moderately rich open cluster in the constellation.
- NGC 2367
- Type: Open Cluster
- Description: A young and compact open cluster.
Canis Minor
Canis Minor is a small constellation. It was included in the 1st century astronomer Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is still included among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "smaller dog" in contrast to Canis Major, the larger dog, and it is commonly represented as one of the dogs following the constellation of Orion the hunter.
The constellation Canis Minor is a small constellation that doesn't contain any Messier objects. The Messier catalog primarily includes star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies, and these tend to be found in larger, more prominent constellations.
However, Canis Minor does have some interesting features, such as its brightest star, Procyon, which is part of the Winter Triangle asterism along with Sirius and Betelgeuse. While there are no Messier objects in Canis Minor, nearby constellations like Gemini and Monoceros do have several.
Gemini
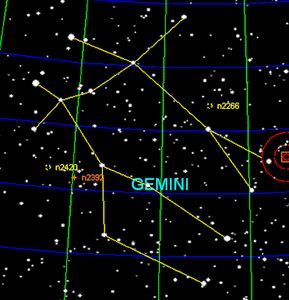
Gemini is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "twins", and it is associated with the twins Castor and Pollux in Greek mythology. Its symbol is (Unicode ?). It lies between Taurus to the west and the dim Cancer to the east, with Auriga and Lynx to the north and Monoceros and Canis Minor to the south.
The Gemini constellation, known as "The Twins," contains several notable Messier objects, which are deep-sky objects cataloged by the French astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th century. However, there is only one Messier object located within the boundaries of the Gemini constellation:
- Messier 35 (M35)
- Type: Open Cluster
- Magnitude: 5.3
- Description: M35 is a large and relatively dense open cluster located in the western part of Gemini, near the foot of one of the twins (Castor). It contains several hundred stars and is about 3,870 light-years away from Earth.
Although M35 is the only Messier object directly within Gemini, neighboring constellations like Cancer and Taurus host additional Messier objects that might be of interest, such as M1 (the Crab Nebula in Taurus) and M44 (the Beehive Cluster in Cancer).
Auriga
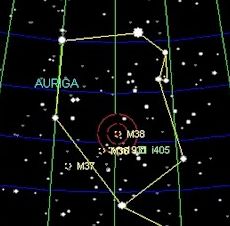
Auriga is a constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'charioteer' and its stars form a shape that has been associated with the pointed helmet of a charioteer. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 1st century astronomer Ptolemy, and is included among the 88 modern constellations. Its brightest star is Capella.
- Messier 36 (M36) - Also known as NGC 1960, this is an open cluster in the constellation Auriga. It is about 4,100 light-years away from Earth.
- Messier 37 (M37) - Also known as NGC 2099, M37 is the brightest and richest open cluster in Auriga. It lies about 4,500 light-years away from Earth.
- Messier 38 (M38) - Also known as NGC 1912, this open cluster is another member of the Auriga constellation. It is approximately 4,200 light-years away from Earth.
Taurus
Taurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for bull, and its symbol is (Unicode ?), a stylized bull's head. Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere's winter sky, between Aries to the west and Gemini to the east; to the north lie Perseus and Auriga, to the southeast Orion, to the south Eridanus, and to the southwest Cetus.
- Messier 1 (M1) - The Crab Nebula
- Type: Supernova Remnant
- Description: The Crab Nebula is the remnant of a supernova explosion that was observed in 1054 AD. It's one of the most studied objects in the sky and lies in the Taurus constellation.
- Messier 45 (M45) - The Pleiades
- Type: Open Star Cluster
- Description: Also known as the Seven Sisters, this open star cluster is one of the closest to Earth and the most easily visible to the naked eye. It contains hundreds of stars, but the brightest ones form a distinctive shape that has been recognized in many cultures.
