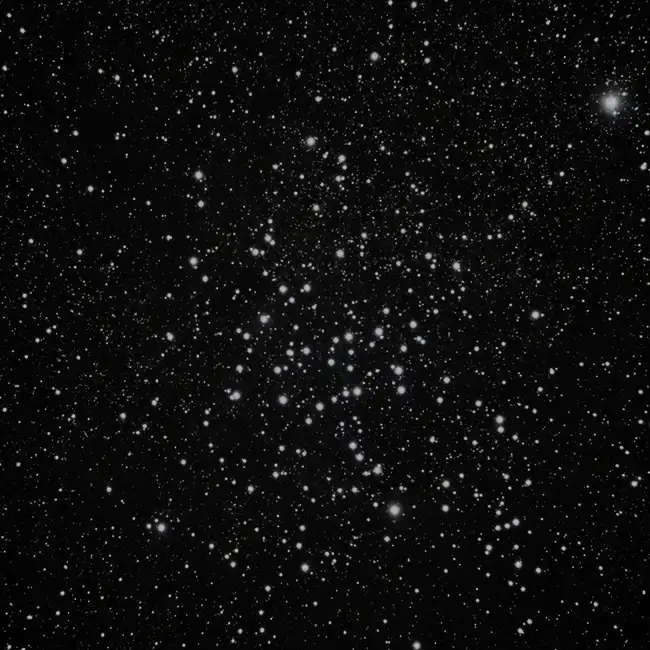
Messier 23 (M23), also known as NGC 6494, is a bright open cluster located in the constellation Sagittarius. It lies at a distance of approximately 2,150 light-years from Earth and spans about 15-20 light-years across. M23 is composed of around 150 to 200 stars, many of which are relatively young, shining brightly with blue and white hues. This cluster offers a stunning view through small telescopes, revealing a rich, scattered pattern of stars.
M23 is an example of an open cluster, a group of stars that formed from the same molecular cloud and remain loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction. These stars are relatively young, estimated to be about 220 million years old. The cluster’s location in the Milky Way's disk means it is situated in a dense region of space, filled with star-forming material and other bright stellar objects.
Magnitude Messier 23 has an apparent magnitude of 5.5, making it visible to the naked eye under dark skies. However, for most observers, it’s better viewed through binoculars or a small telescope, which will reveal the cluster's individual stars and intricate patterns. The brightest stars within M23 have magnitudes of around 9.2, making them easy targets for amateur astronomers.

Season and Prominence
M23 is best observed during the summer months when the constellation Sagittarius is prominently visible in the night sky. For observers in the Northern Hemisphere, the cluster is ideally positioned between June and September. Sagittarius is located low in the southern sky, making this a prime summer target.
In the Southern Hemisphere, M23 is even more easily observed, given that Sagittarius is higher in the sky. Observers there can enjoy an extended viewing period throughout the winter months.
Constellation
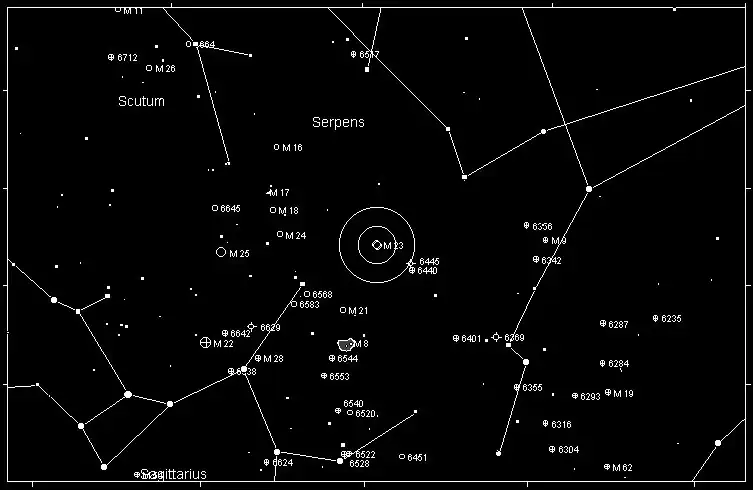
Messier 23 is located in the constellation Sagittarius, often referred to as "The Archer." Sagittarius is a rich and complex constellation, known for being home to many deep-sky objects, including star clusters, nebulae, and the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Sagittarius is often associated with the famous "teapot" asterism, which helps observers locate objects within the constellation.
How to Find M23
To locate Messier 23, start by finding the Sagittarius constellation, which is most easily identified by the teapot-shaped asterism. M23 is situated north of the teapot, slightly west of the bright star Mu Sagittarii (μ Sgr). From there, trace your telescope about 1.5 degrees northwest to the cluster’s location.
If you are using binoculars, scan the region just above and to the right of the spout of the teapot. With a small telescope, M23 will appear as a faint, fuzzy patch, and with higher magnifications, the individual stars of the cluster will start to resolve.
History
Messier 23 was discovered by the French astronomer Charles Messier on June 20, 1764. As part of his famous catalog of nebulous objects, M23 was added not as a nebula but as a star cluster. Messier cataloged such objects to help astronomers distinguish them from comets, which he was hunting. The Messier catalog eventually became one of the most famous lists of celestial objects, widely used by amateur and professional astronomers alike.
While Messier 23 itself hasn’t been the subject of many groundbreaking studies, it remains an important object for understanding star formation and evolution. The study of open clusters like M23 helps astronomers better understand the processes that lead to star formation and the early lives of stars.
Conclusion
Messier 23 is a bright and accessible open cluster that offers stunning views for amateur astronomers, especially during the summer months. Located in the constellation Sagittarius, M23 provides an excellent target for both binocular and telescope users. Its history as a part of the Messier catalog and its position within the rich star fields of the Milky Way make it a fascinating object to observe and study. Whether you are a seasoned astronomer or a beginner, M23 is a rewarding celestial treasure to add to your observing list.
