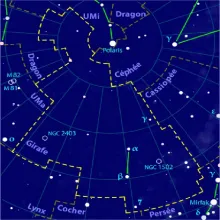
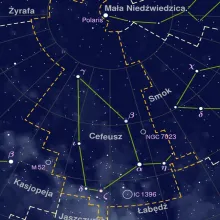
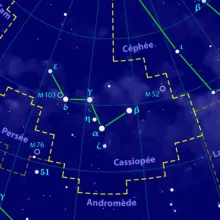
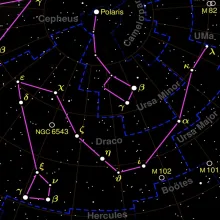
Constellation Camelopardalis
Camelopardalis is a faint and large constellation located in the northern sky. Its name is derived from the Latin word for "giraffe," which itself comes from the Greek words "kamēlos" (camel) and "pardalis" (leopard), due to the giraffe's long neck and spotted coat. The constellation is relatively obscure and consists of faint stars, making it a challenge to spot without clear, dark skies.