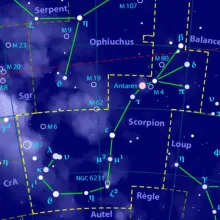
Constellation Scorpius
Scorpius is one of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky, known for its distinct shape resembling a scorpion. It is a prominent constellation in the Southern Hemisphere and is best observed during the summer months.
Scorpius is a large constellation that stretches across the sky, with its most notable feature being the curved line of stars that form the scorpion's tail and the bright star Antares at the heart of the scorpion. The constellation is located near the Milky Way, making it a rich area for stargazing with numerous star clusters and nebulae visible.